
NPS The word “Bacteria” is often associated with disease, but only a few kinds of Bacteria (species) cause problems for humans. The other millions of bacterial species, although all simple organisms, play a complex role in Earth’s ecosystems. In fact, Cyanobacteria were responsible for the oxygenation of our atmosphere. They were the first photosynthesizers, converting light energy into oxygen more than 2.4 billion years ago. Without Bacteria, in particular Cyanobacteria, humans would not be able to breathe and we would therefore not be here. While some Bacteria perform photosynthesis, others depend on chemical energy that is released when unusual compounds like hydrogen, arsenic, or sulfur react with oxygen. This energy is then used to convert carbon dioxide into biomass (chemosynthesis). For example, the bacterium, Thermus, may also be able to oxidize arsenic into a less toxic form to humans. Individual Bacteria may be rod or sphere shaped, but they often join end to end to form long strands and streamers (filaments) that are often seen in the outflow channels of hot springs. These strands help form thermophilic mats, forming a vast community or mini-ecosystem. Other groups of Bacteria form layered structures resembling tiny towers, that can trap sand and other organic materials. Source: NPS DataStore Collection 7681. To search for additional information, visit the NPS DataStore. 
Thermophilic Archaea
Archaea are the most extreme of all extremophiles. 
Thermophilic Eukarya
Microscopic plants and animals live in the extreme environments of Yellowstone's hydrothermal features. 
Thermophilic Viruses
Viruses, a logical part of thermophilic ecosystems, have been found in some pools in Yellowstone. 
Thermophilic Communities
Thermophilic communities are very diverse, depending on the microbes living there, the pH, and the water temperature. 
Thermophiles in Time and Space
Yellowstone's hydrothermal features and thermophilic communities are studied by scientists searching for evidence of life on other planets.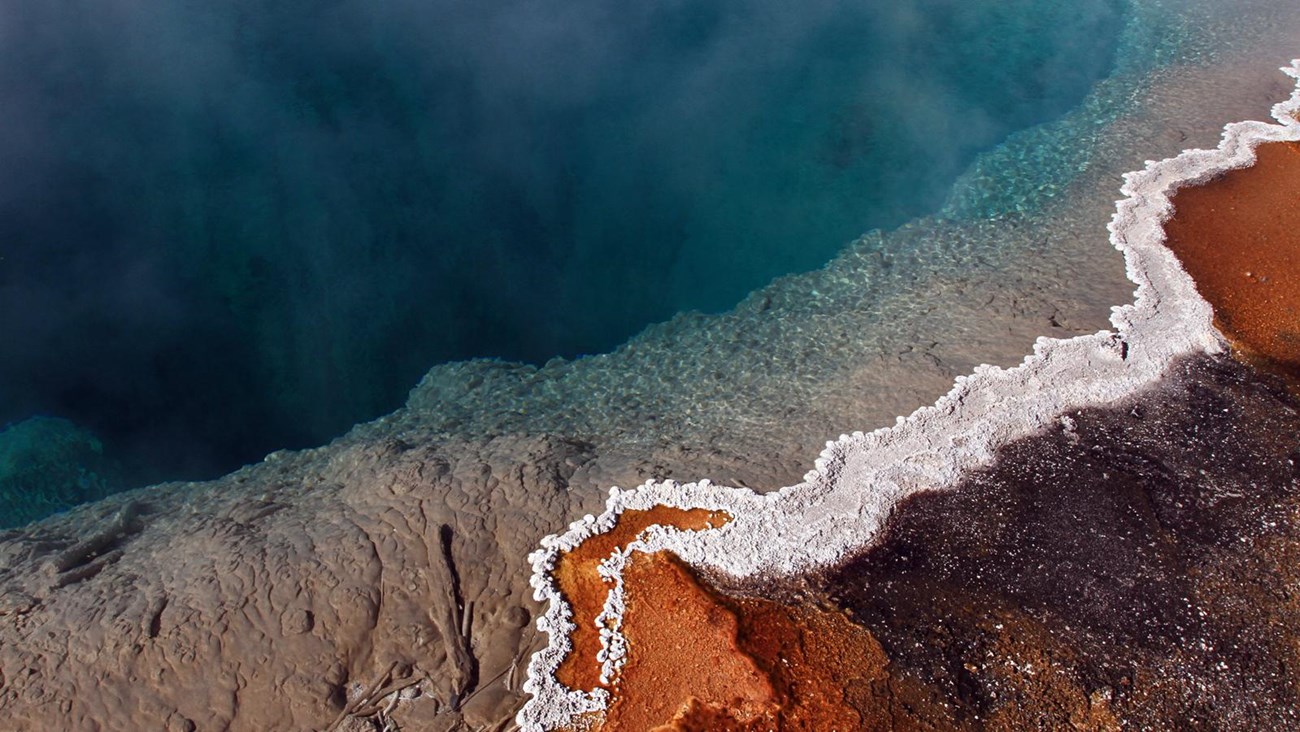 
Life in Extreme Heat
Hydrothermal features are habitats for microscopic organisms called thermophiles: "thermo" for heat, "phile" for lover. |
Last updated: April 18, 2025
