Scientists, students, volunteers develop fresh insights at the Giacomini Wetlands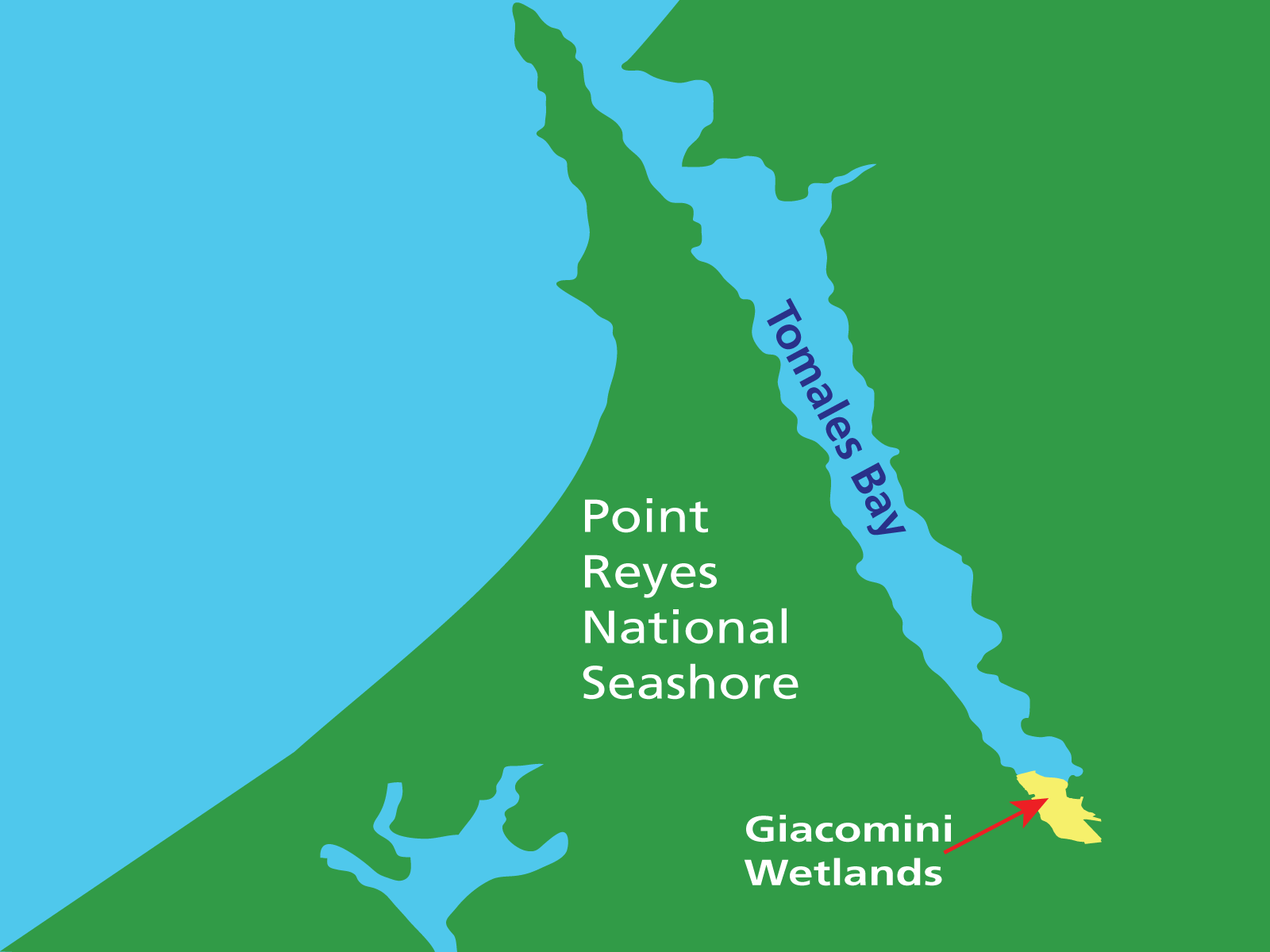
NPS Image. The Internet is not omniscient. Natural areas harbor unrecorded answers to questions yet to be asked. For instance, the Giacomini Wetlands offer fresh understandings about threatened animals and climate change. Scientists, students and volunteers converge increasingly at this new nexus for research. The wetlands once resonated with the sound of cattle lowing. During the early 1900s levees were built to control the waters of Tomales Bay, about a one-hour drive north of San Francisco. The resulting dry land provided range for dairy cows. But drainage curtailed the natural services that wetlands had previously provided. These lost amenities included floodwater retention, water cleansing, wildlife sustenance and recreation. In 2000, the National Park Service acquired the Waldo Giacomini Ranch in order to restore the wetlands. Alongside partners, they built new habitats and tore down a levee. With the inflow of tidal waters the wetlands' natural services resumed. Now researchers take to the wetlands for answers to new questions. "The work needs many hands," said Laurie Hall, an environmental scientist at Humboldt State University in Arcata, California. She enlisted undergrads and interns to help canvas the wetlands of the Bay Area at night in search of secretive marsh birds. To participate in activities similar to those of researchers, youth come from around the San Francisco Bay area. Five hundred students registered to visit the Giacomini Wetlands in 2016. They follow scientific procedures using microscopes, binoculars and spotting scopes to observe sediment, plants, invertebrates and birds. "Once they start looking at birds with the instruments that we provide for them, they can appreciate what a bird is and the value of birds," said Leslie Adler-Ivanbrook, manager of the Science at the Seashore program with the Point Reyes National Seashore Association. "They start understanding the value of the birds in their own environment." The wetlands and Tomales Bay hold answers to questions about how a mouse-sized bird takes up residence in a new place, how aquatic plants sequester carbon, and how a state amphibian uses its habitat. How do California black rails disperse among isolated wetlands in the Bay Area?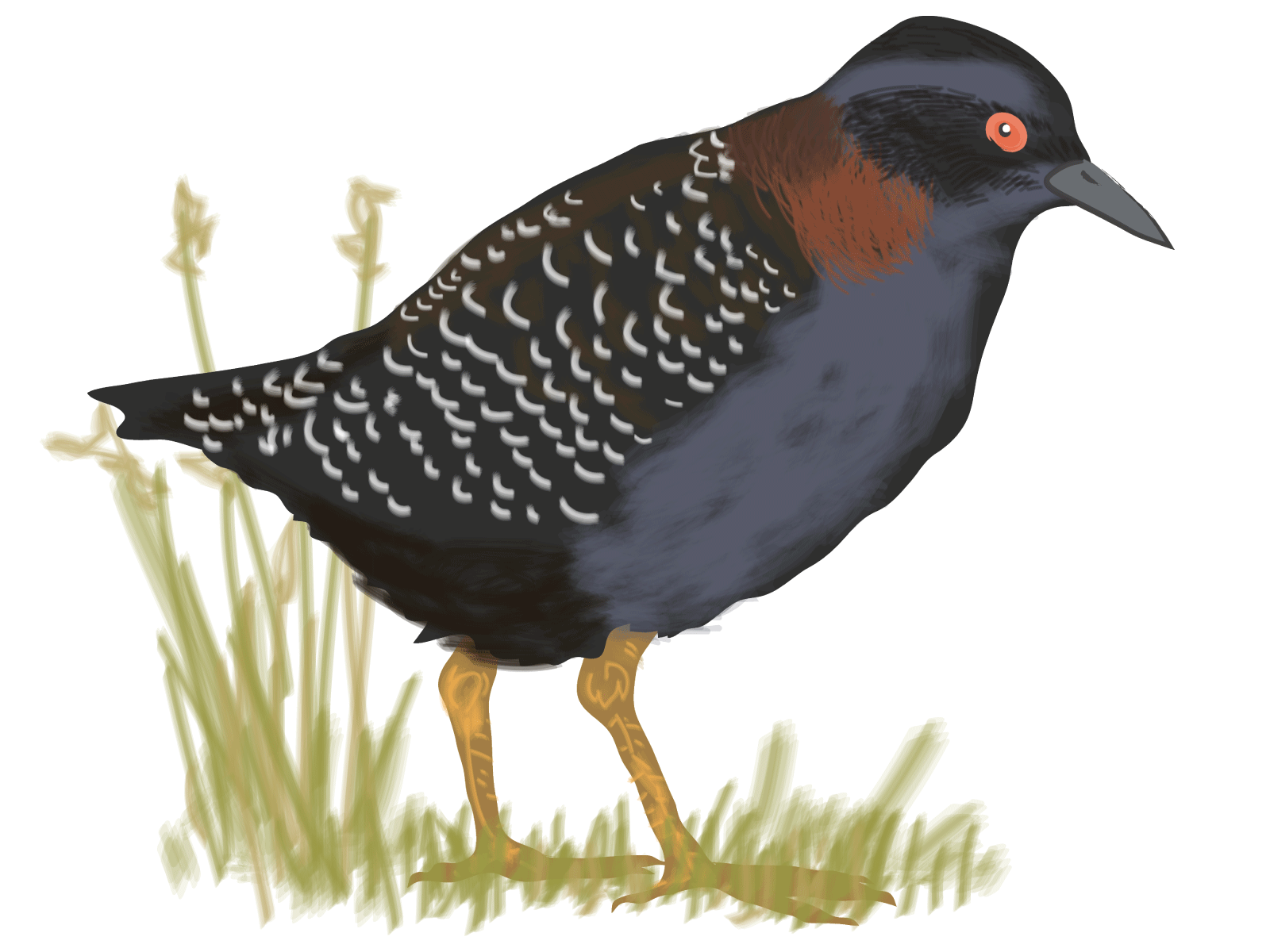
NPS Image. "Rails are some of the most elusive and poorly understood birds. Few studies have directly quantified their dispersal distances," Hall said. The California black rail, a rare wetland bird, is state-listed as threatened. Historically, black rails were quite abundant around Tomales Bay. But loss of their wetland habitat decreased the number of rails. And loss of nearby wetlands isolated the Giacomini Wetlands, Hall said. She wanted to discover how far rails disperse throughout the larger San Francisco Bay Area. Volunteers pitched in to help from Point Blue Conservation Science, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, the National Park Service and the public. Many citizen scientists had never been involved in research or had even seen a black rail, Hall said. Hall found that the birds' dispersal, which is important for sustaining the population, did not seem hampered by the relatively isolated, wetland habitat at Giacomini. "But future changes in Bay Area wetlands caused by development will be exacerbated by sea level rise," she said. The Giacomini Wetlands have been protected from development, but not from sea level rise. Would the rail's ability to disperse under isolated conditions help it to survive sea level rise? Future tromping through the wetlands may yield the answer to this question. Would "blue carbon" combat climate change in California?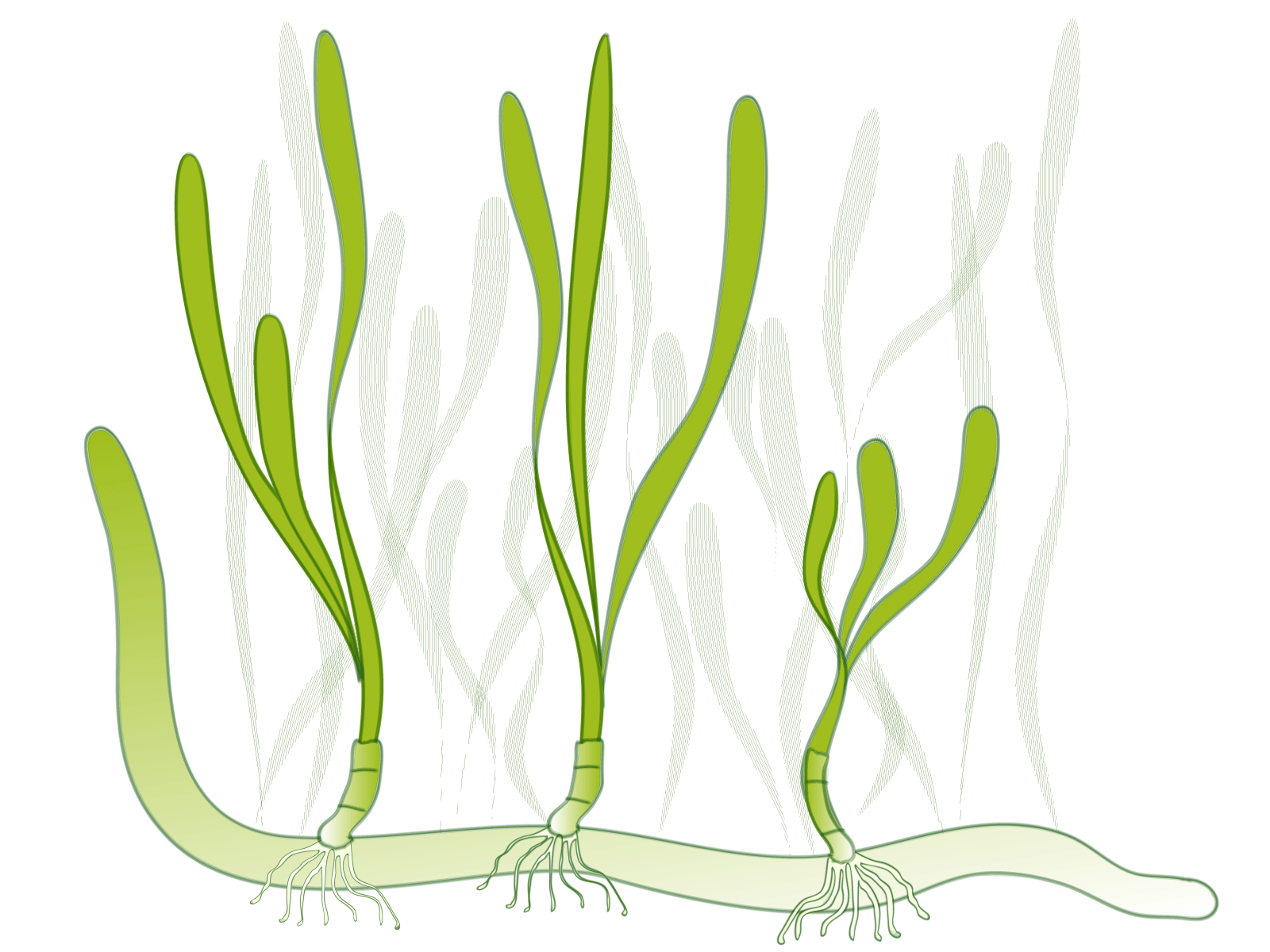
NPS Image. Brady O'Donnell, a graduate student at the University of California, Davis, studies how coastal ecosystems combat climate change. He monitors research plots in Tomales Bay, including one close to the wetlands. Earth's climate is changing due to mounting carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the air. Humans spew these gasses into the atmosphere when they burn coal, oil, and other fossil fuels. These gasses act like a blanket around our planet. They hold in the Sun's heat and do not let much escape. The oceans, like a giant sponge, absorb about one third of this carbon dioxide, O'Donnell said. Mangroves, seagrasses, and other ocean plants—called "blue carbon"—use carbon dioxide to grow leaves, roots and stems, he said. Sand and clay may cover the plants when they die. In this process sediments may bury more than 1,000 pounds of plant-based carbon per acre each year, according to the Verified Carbon Standard. The VCS aims to work with leaders worldwide to reduce greenhouse gases. Scientists have studied blue carbon around the world, said O'Donnell. However, he is carrying out the first study in California that looks at seagrasses. He wants to determine how the density of the plants affects their rate of carbon burial here. He also wants to find out whether the carbon stays buried, he said. If O'Donnell finds that seagrass beds bury significant amounts of carbon in California, then policies to protect seagrass habitat may ameliorate the effects of climate change in Tomales Bay, he said. "Creative opportunities to address climate change may provide part of the solution in the present time," O'Donnell said. At the Giacomini Wetlands, fourth-graders use the same kind of sieves that O'Donnell uses when he separates plant material from shells at Bodega Marine Lab. The students also roll sediment between their hands and sniff decomposing plants. Such activities may someday help them comprehend the concept of blue carbon. How do threatened California red-legged frogs use their habitat?
NPS Image. The California red-legged frog--the state amphibian--abounds in the Giacomini Wetlands and surrounding area, said Patrick Kleeman, an ecologist with the U.S. Geological Survey, Point Reyes. But in 1996 the frogs were federally listed as threatened under the Endangered Species Act. Their wetland habitats are in decline statewide. "We've been trying to figure out how they use their habitat so that land managers can better learn how to protect them," Kleeman said. Kleeman led citizen scientists through the Giacomini Wetlands during BioBlitz 2014. His group volunteered to document as many amphibians as they could during the 24-hour event sponsored by the National Geographic Society and the National Park Service. "It was a bit of a misty evening," Kleeman said, "a good evening for amphibians to be out and about." He warned his group that they were unlikely to see California red-legged frogs, which frequented a deeper pond than they were going to go near. As they started their walk, he said, a little boy headed down the path in front of him. Kleeman said soon the boy asked, "What's this frog down here?" It was an adult California red-legged frog. "I caught it and showed it to everybody," Kleeman said, "and then let it go its own way to carry out its little happy life." When land managers create the right habitat, California red-legged frogs may move in and multiply. Using radio transmitters to monitor the amphibians, Kleeman documented that some may travel more than three-fourths of a mile from their breeding ponds. Before restoration, he had found none of the frogs in a particular location. But in 2014, he counted 35 adult frogs and their eggs at the same site—improved habitat at the Giacomini Wetlands. Adler-Ivanbrook works closely with teachers to integrate fieldwork with their classroom science curriculum. Yet when students take delight in a frog, they absorb more than scientific principles or, possibly, career inspiration. They learn to care for the wetlands, she said. "They always say they want to come back to the wetland." Scientific processes and instruments engage the senses. For those who seek fresh understandings at the Giacomini Wetlands, physical observations may give way to a new, synthesized perception. The angle at which the morning sun softens frost that has formed on emerging grasses, the distant scent of saltwater, the clack of fennel shaken by a blast of winter wind—all comprise a figurative sense of place. A sense of place may yield to a sense of wonder. And a sense of wonder may lead to yet another offline quest at the Giacomini Wetlands. --- 1.4 Mg ~ 3086 pounds, ~1.5 U.S. tons |
Last updated: June 22, 2025
