Last updated: January 19, 2023
Place
Site of the Austin Bearse Home
Norman Leventhal Map Center, Boston Public Library
No longer standing, this is the site of the home of Austin Bearse, a key contributor to Boston’s Underground Railroad. Born in Barnstable, Massachusetts, Bearse found early employment working with ships that traded with the South. Within this trade, Bearse witnessed the evils of slavery and dedicated his life to the abolitionist movement. Relocating to Boston, Bearse utilized his maritime skills to assist fugitives escaping from enslavement. Bearse used his ship, The Moby Dick, to intercept freedom seekers that had stowed away on southern ships that came to Boston. For example, in September of 1854 Bearse received a tip that a ship called the Sally Ann had a stowaway on board. As Bearse recalled,
I made sail for City Point, South Boston. I landed the slave and carried him up to my house, stripped off his old tow suit and dressed him in another so he could not be known…Had just got him ready when Mr. Samuel May, Jr. and Dr. S. Cabot drove up to my house with a carriage, took him and carried him to the Boston Worcester Depot, and Mr. May went on with him to Worcester, and from there he was sent on the underground railway to Canada.1
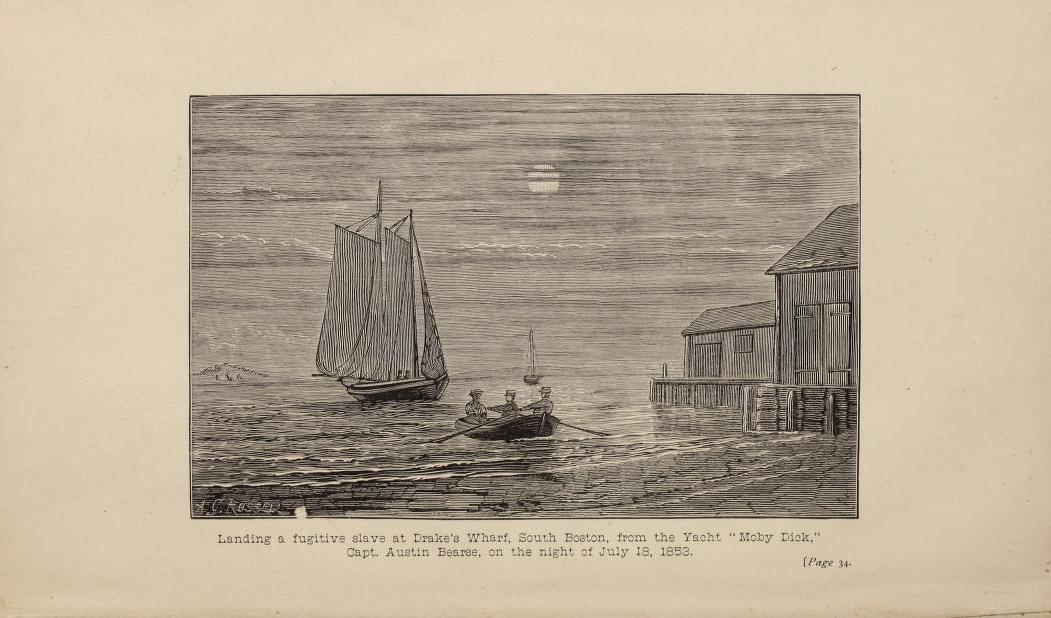

"Landing a fugitive slave at Drake's Wharf, Boston, from the Yacht 'Moby Dick,' Capt. Austin Bearse, on the night of July 18, 1853."(Credit: Reminisces of the Fugitive Slave Law Days, 1880)
Learn more...
Maritime Underground Railroad.
Footnote
- Austin Bearse, Reminisces of the Fugitive Slave Law Days. (Boston: Warren Richardson, 1880) 36-37. Archive.org
