|
The height of prehistoric occupation of the Tonto Basin occurred when the Salado, a group of sedentary agriculturists, occupied the area from about A.D. 1150 to 1450. This period is represented not only by the Upper Dwelling, Lower Dwelling, and Lower Dwelling Annex, but also by many other smaller sites. The site type designations are rock shelter, field house, 2-5 room site, and large pueblo. 
Rock sheltersThe rock shelters are broken down into two subgroups: large multi-room rock shelters and small single-room caves. The large multi-room rock shelters include those shelters with interior architecture, as well as those with natural chambers. The second group of rock shelters includes small one-room caves with little or no cultural modifications. 
Field HousesSingle room structures were commonly called field houses and may have been associated with the tending of agricultural fields. 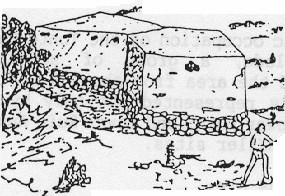
2-5 Room StructuresSites of this type were common in the Tonto Basin. The rooms are generally square or rectangular 3 or 4 sided cobble foundations from one to four layers high. The rooms were either contiguous or in close proximity. 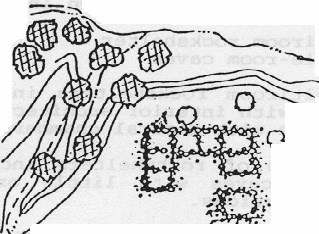
Large PueblosLike the features identified at the smaller sites, these were made of layered walls of unshaped cobbles. The lack of large amounts of wall fall surrounding them indicates perishable superstructures of wattle and daub. Some sites include 6-8 continuous rooms as well as noncontiguous structures. |
Last updated: June 15, 2021
