Mining and ranching changed how people used the land around Joshua Tree. The California Gold Rush and successful cattle ranching made the southwest deserts more appealing. Beginning in the 1870s, gold miners came to the rocky hills around Twentynine Palms, while ranchers used the highlands for spring grazing and built water catchments called “tanks” to capture water for the cattle.
The arrival of new groups deeply impacted Native American communities, cutting them off from their traditional food resources, water sources, and place-based culture. Pressured to leave traditional collecting and travel areas for nearby designated reservation lands, Serrano, Cahuilla, Chemehuevi, and Mojave communities lost access to traditional resources outside of these designated areas. Some tribal members adapted by working for early prospectors or were hired as farm hands and cowboys.
Today, nearly 300 historic mines are located in the park. Important ranching locations like Quail Springs, Hidden Valley, and Barker Dam are popular sites for visitors. Indigenous footpaths became wagon tracks and are now current roads.
Ranching
-
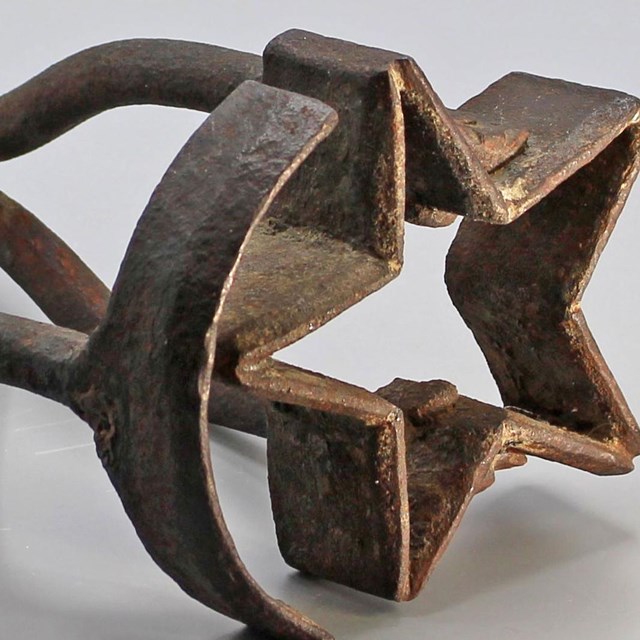 Brand
BrandJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 35978
-
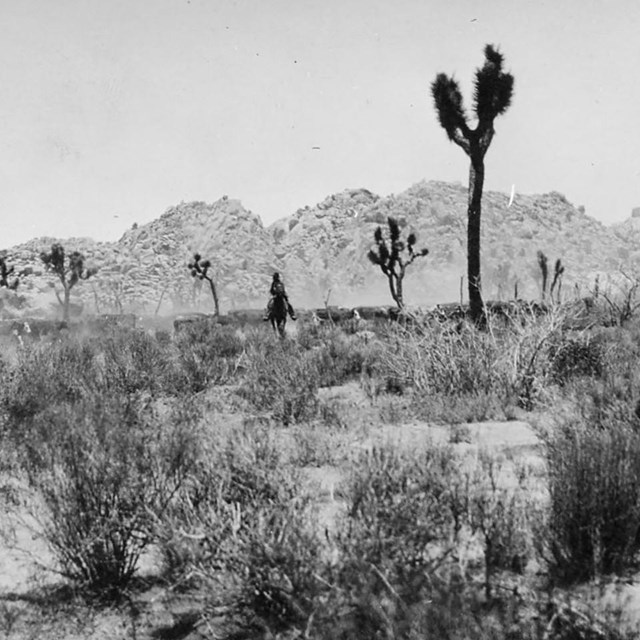 Shea driving cattle
Shea driving cattleJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 531
-
 Notice of Water Appropriation
Notice of Water AppropriationJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 24757
-
 Willow Hole
Willow HoleNational Park Service photograph
-
 Shotgun
ShotgunJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 2622
-
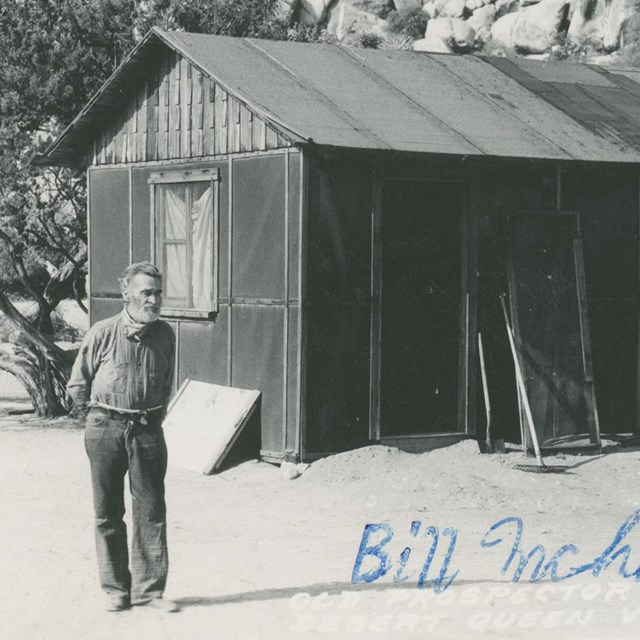 Bill McHaney in front of cabin
Bill McHaney in front of cabinJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 40127, Box 3
-
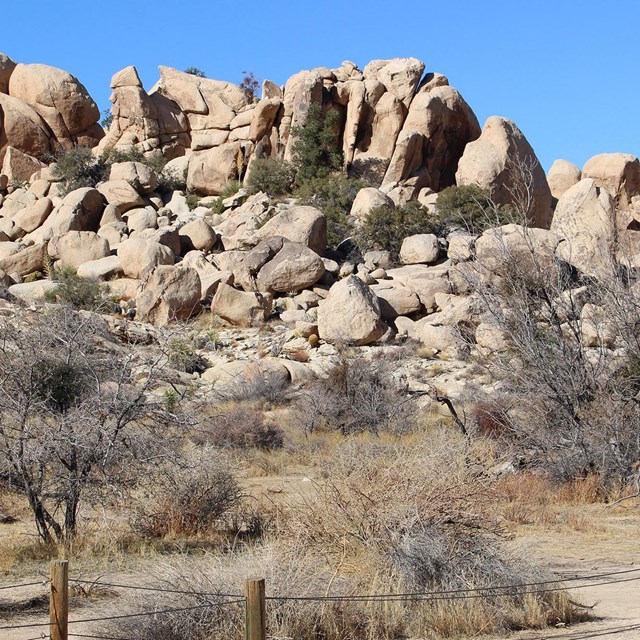 Looking toward the site today
Looking toward the site todayNational Park Service photograph
-
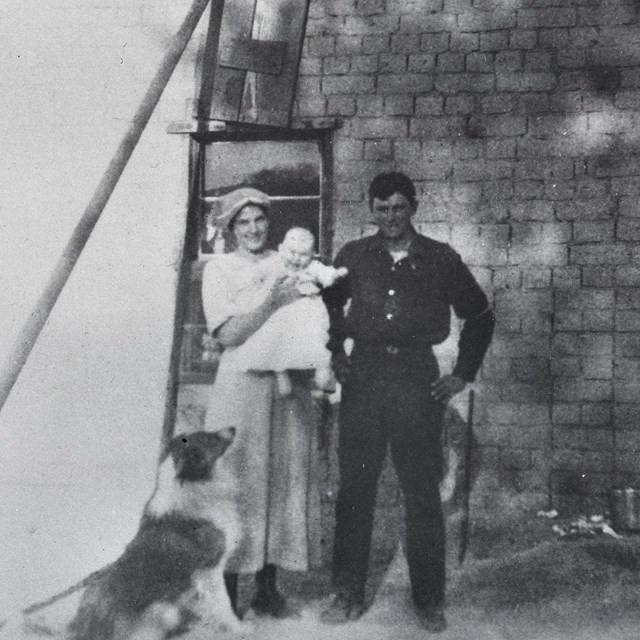 Joe Pachecco and family
Joe Pachecco and familyJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 20575, image #1648
Mining
-
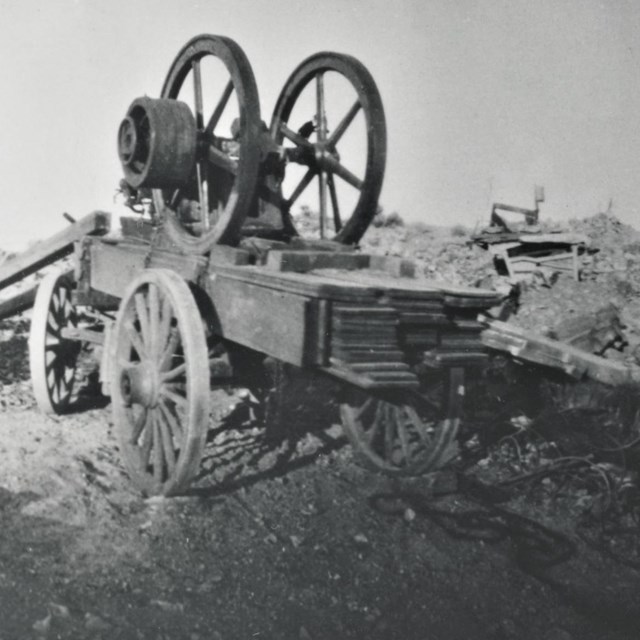 Desert Queen Mine
Desert Queen MineJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 20575 #2407
-
 Location Notice (Mining Claim) and Jar
Location Notice (Mining Claim) and JarJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 29981
-
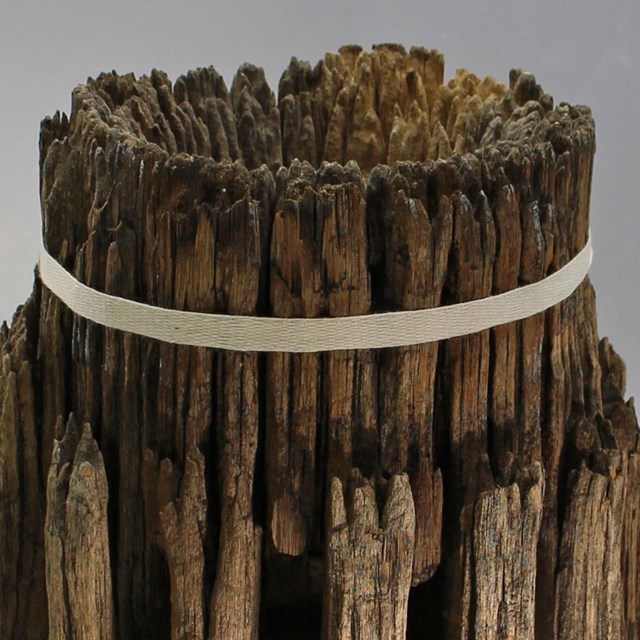 Central Wheel Hub, Pinto Wye Arrastra
Central Wheel Hub, Pinto Wye ArrastraJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 35966
-
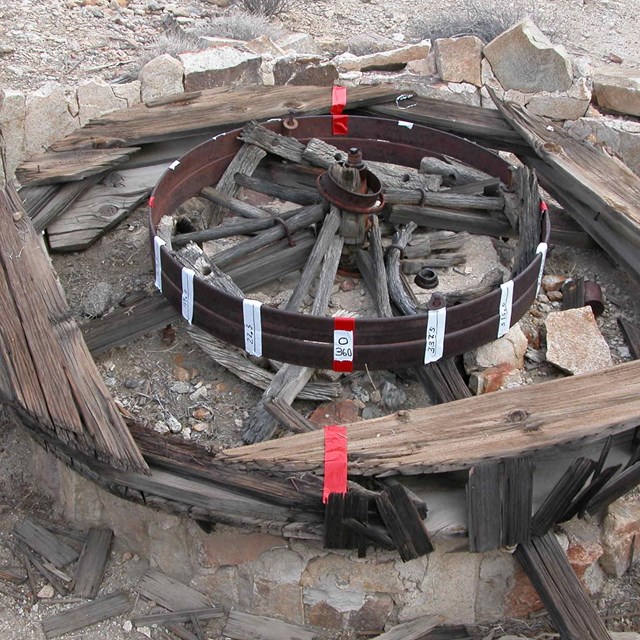 Documenting arrastra before preservation
Documenting arrastra before preservationNational Park Service photograph
-
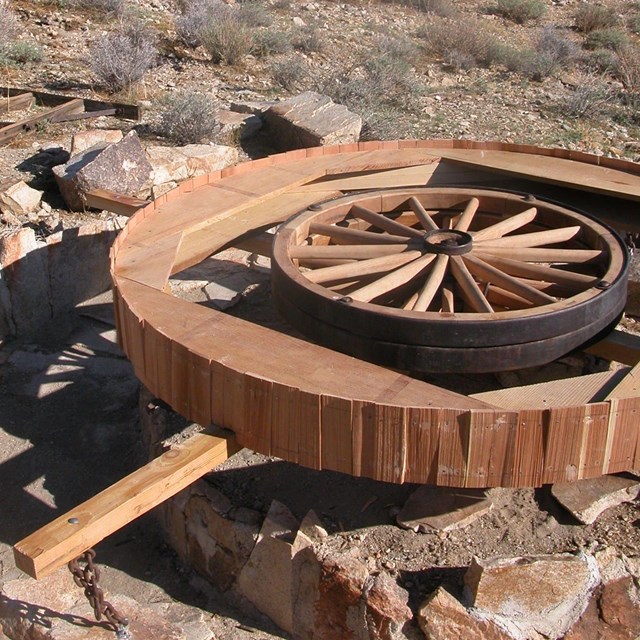 Pinto Wye Arrastra after preservation
Pinto Wye Arrastra after preservationNational Park Service photograph
-
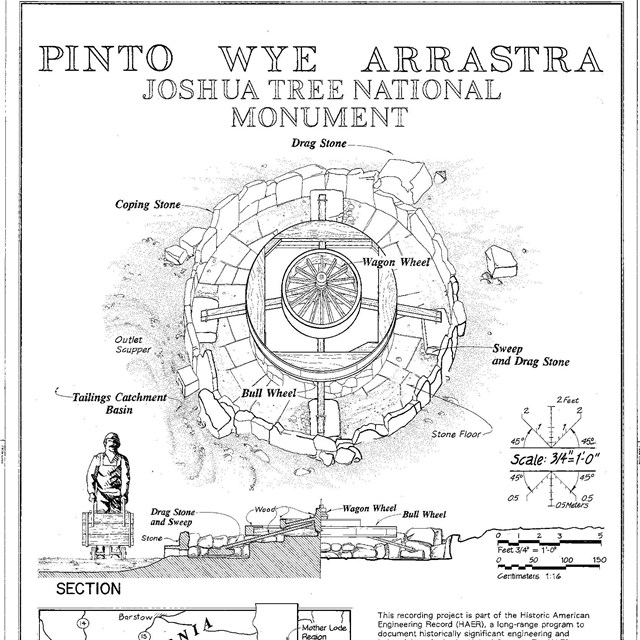 Pinto Wye Arrastra HAER drawing
Pinto Wye Arrastra HAER drawingHistoric American Engineering Record, HAER CAL,36-TNPAL.V,4- (sheet 1 of 2)
-
 Shoe Stamp
Shoe StampDesert Queen Ranch Collection
-
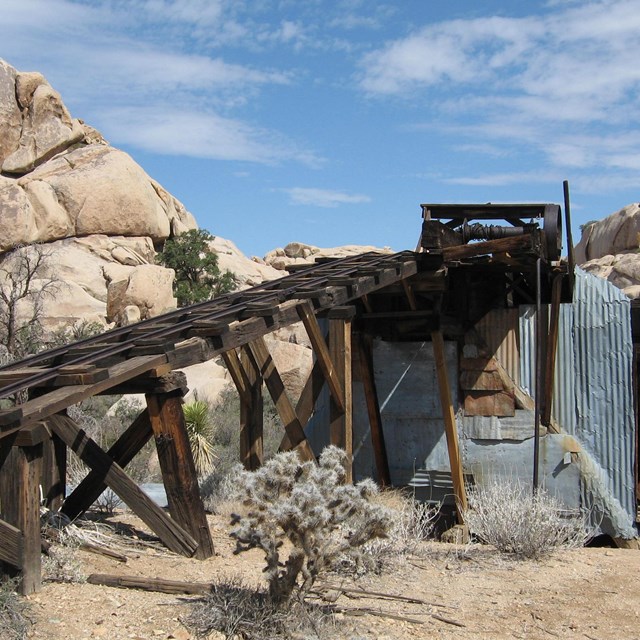 Wall Street Mill
Wall Street MillNational Park Service photograph
-
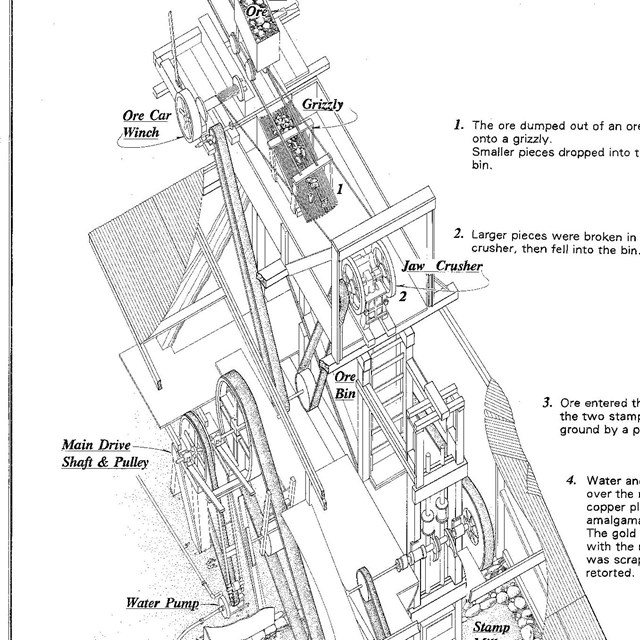 Wall Street Gold Mill Process Drawing
Wall Street Gold Mill Process DrawingHistoric American Engineering Record, HAER CAL,36-TNPAL.V,2- (sheet 8 of 9)
-
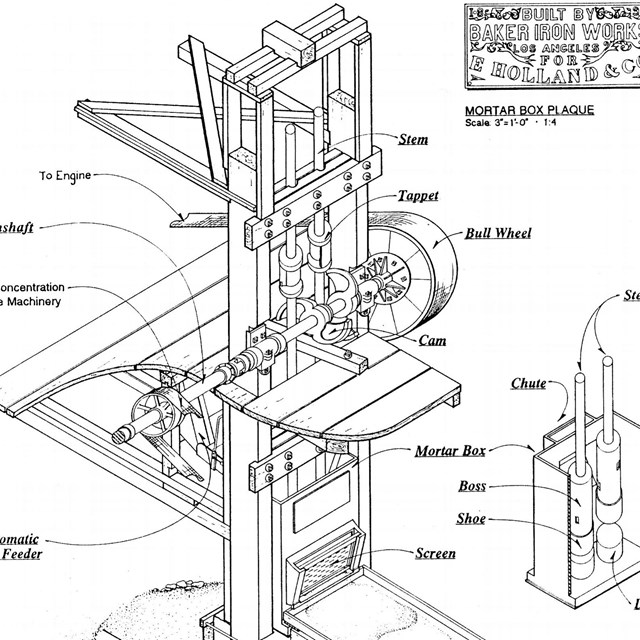 Stamp Battery Axonometric Drawing
Stamp Battery Axonometric DrawingHistoric American Engineering Record, HAER CAL,36-TNPAL.V,2- (sheet 9 of 9)
-
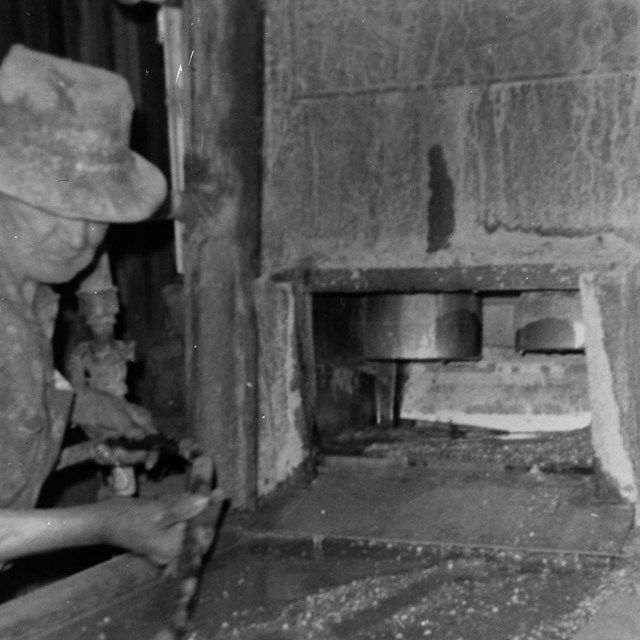 Bill Keys Cleaning Up after Mill Run
Bill Keys Cleaning Up after Mill RunHistoric American Engineering Record, HAER CAL,36-TNPAL.V,2--36
-
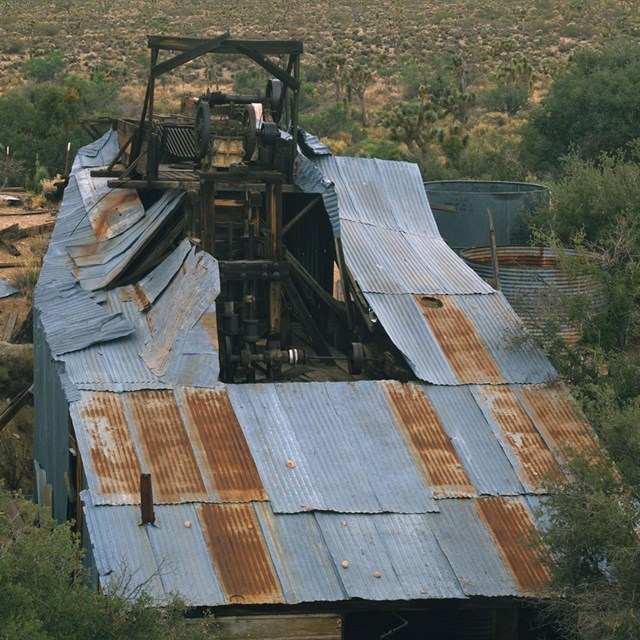 Wall Street Gold Mill, 1991
Wall Street Gold Mill, 1991Historic American Engineering Record, HAER CAL,36-TNPAL.V,2--39 (CT)
-
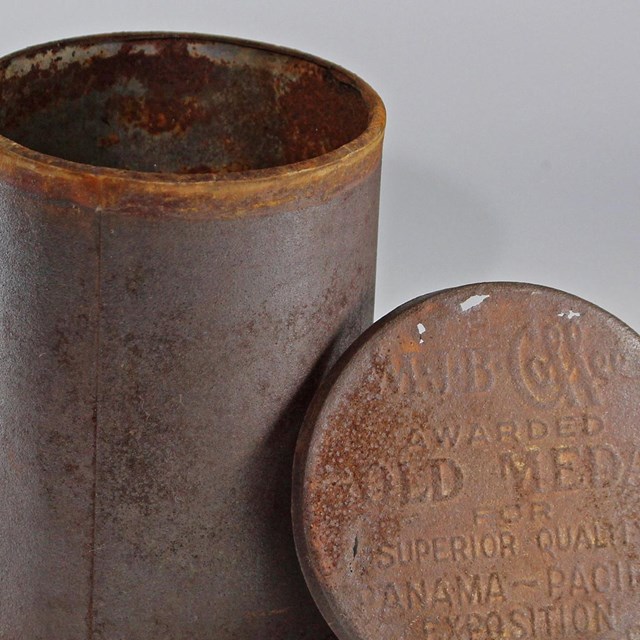 Coffee Tin
Coffee TinJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 31261
-
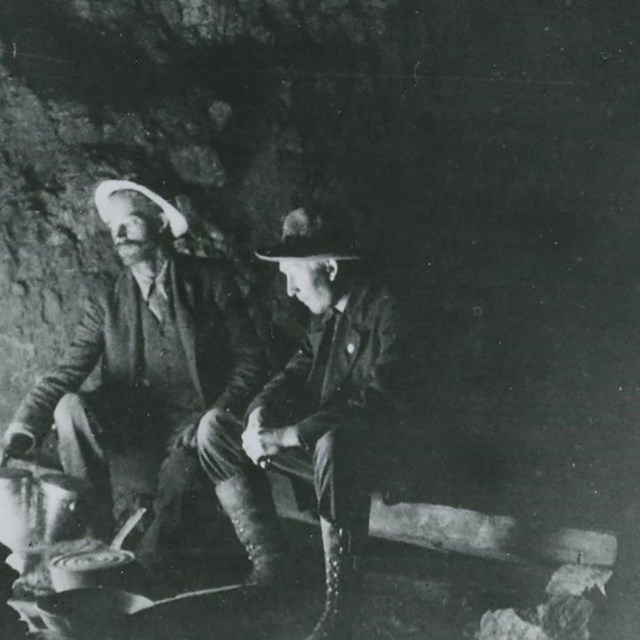 Chester Pinkham and unidentified man
Chester Pinkham and unidentified manJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 20575 #1620
-
 Freight Wagons at Lost Horse Wells
Freight Wagons at Lost Horse WellsJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 20575 #1618
-
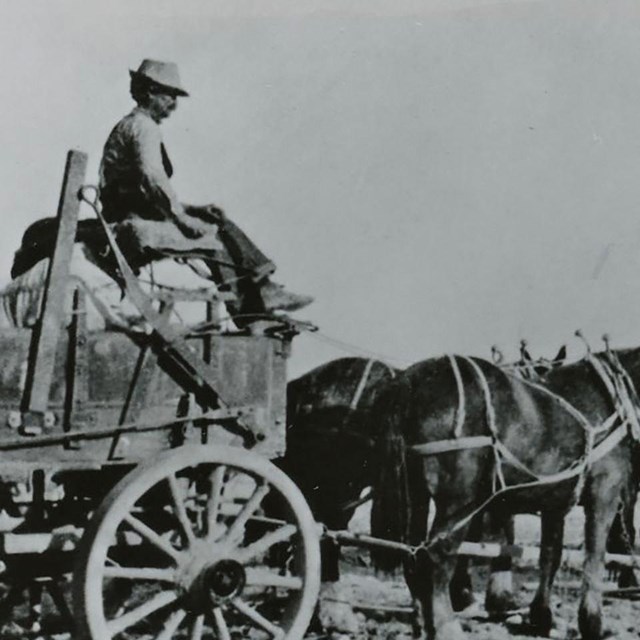 Freighting from Banning to Dale Mine
Freighting from Banning to Dale MineJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 20575 #1625
-
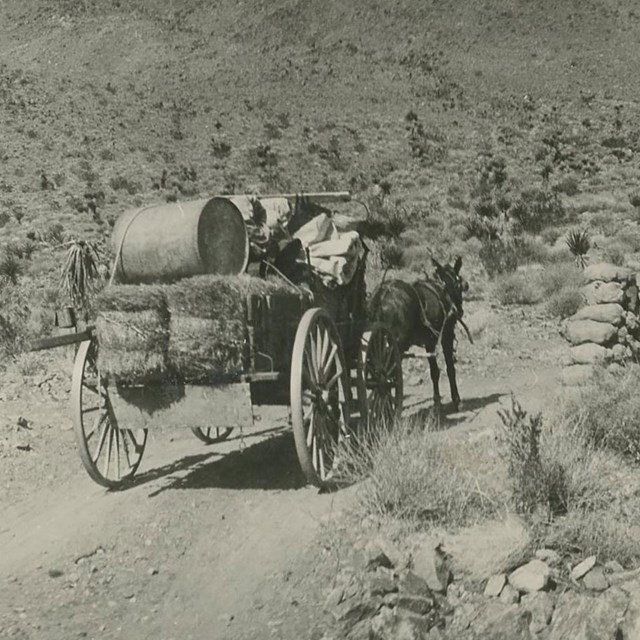 Keys Ore Haul
Keys Ore HaulJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 40127
-
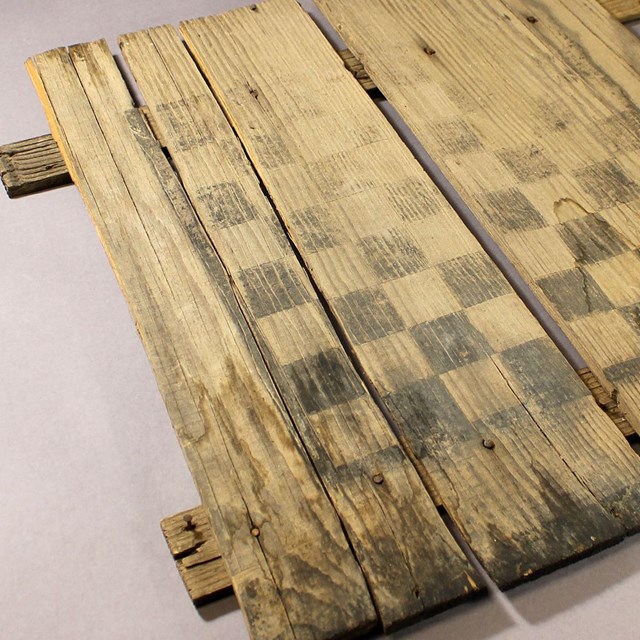 Game Board
Game BoardJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 8754
-
 Gold Ore Sample
Gold Ore SampleJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 1325
-
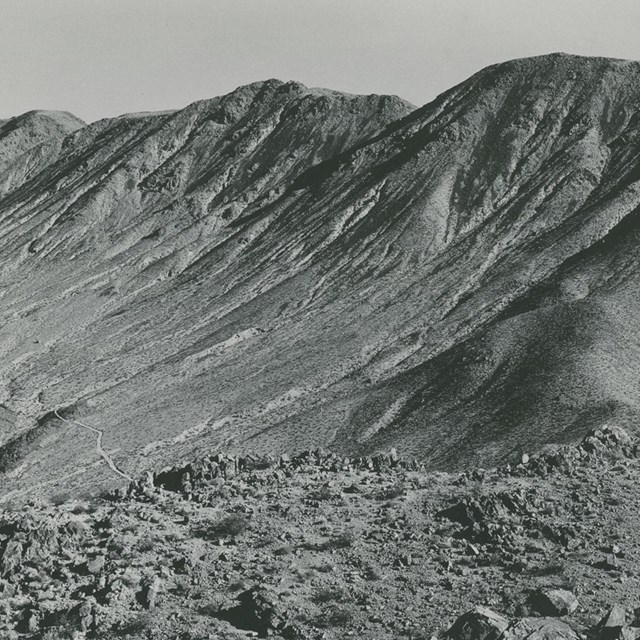 Photograph of the Ivanhoe Mine Area
Photograph of the Ivanhoe Mine AreaJoshua Tree National Park, JOTR 20575, #2048
-
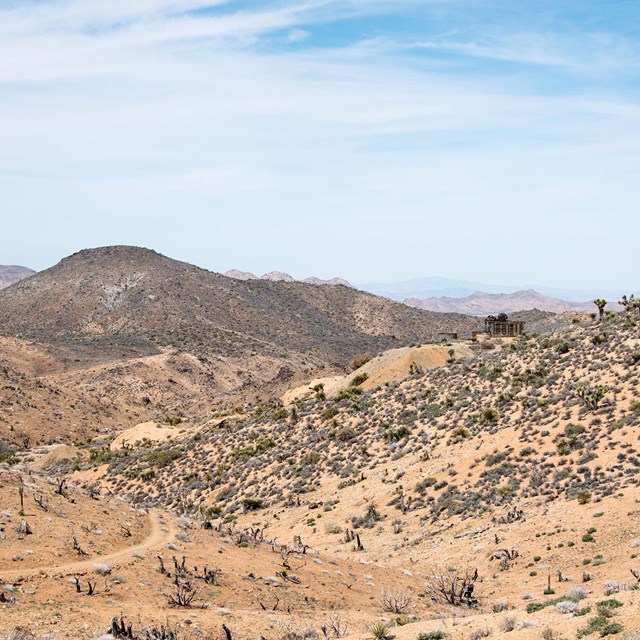 View from the Lost Horse Mine
View from the Lost Horse MineNational Park Service photograph
-
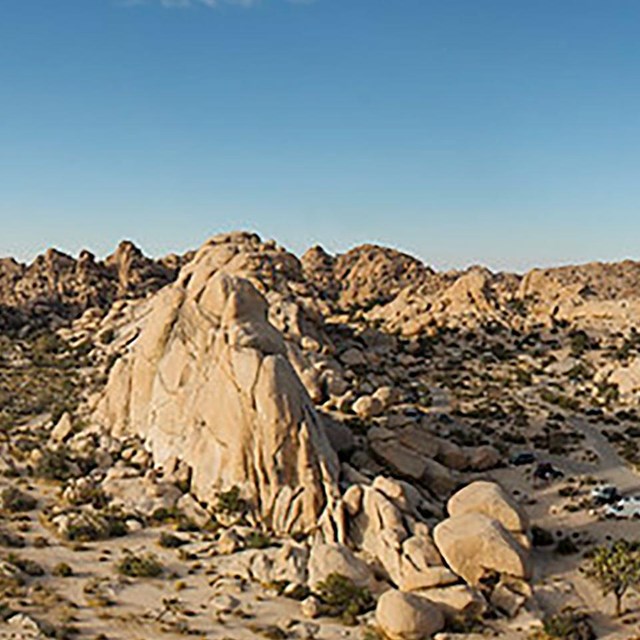 Panorama from top of Intersection Rock
Panorama from top of Intersection RockNational Park Service photograph
-
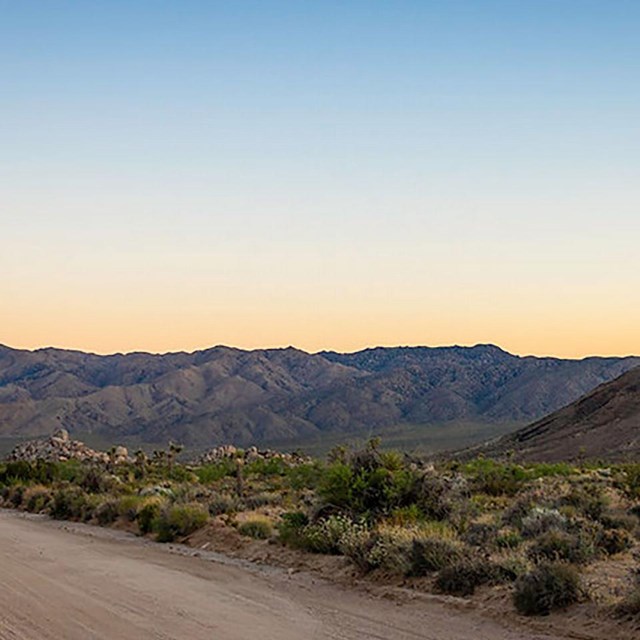 View towards Malapai Hill
View towards Malapai HillNational Park Service Photograph
Last updated: August 10, 2023

