Last updated: April 11, 2024
Article
Weather and Climate Monitoring at Devils Postpile National Monument

NPS / Monica Buhler
Information on day-to-day changes in temperature, precipitation, windspeed, and other variables, or weather, is important for visitors planning trips to Devils Postpile National Monument (DEPO), and for helping monument managers understand short-term variation in natural processes and resources. For example, the behavior of wildfires is affected by variation in daily weather. Long-term characteristics of atmospheric conditions, or climate, are also important to monitor, as climate is one of the most important broad-scale drivers influencing the Sierra Nevada ecosystem. Climate influences the distribution of plants and animals, snowpack and streamflow dynamics, and fire regimes. Warming temperatures related to climate change are resulting in a decrease in Sierra Nevada snowpack water content and earlier melt of the snowpack in the spring. These patterns lead to less water available to plants, animals, and California communities and agricultural areas. Some changes in animal distributions over the past century (shifts upward in elevation for some small mammal species) and increases in tree mortality rates in recent decades are associated with warming temperatures.

NPS / Jeff Balmat
Long-term Monitoring
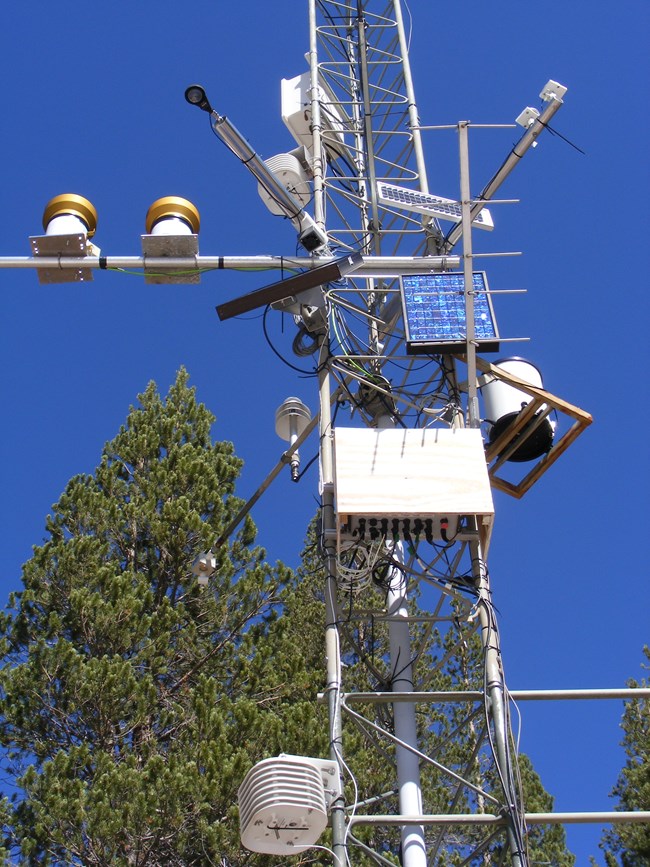
Weather & climate and snowpack were prioritized for monitoring as part of the Sierra Nevada Network long-term monitoring program. The Sierra Nevada Network (SIEN) is a collaborative Inventory & Monitoring program among DEPO, Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks (SEKI), and Yosemite National Park (YOSE). In 2005, National Park Service (NPS) staff at DEPO, SEKI, and SIEN worked with the California Department of Water Resources and Scripps Institution of Oceanography to install a weather monitoring station at Soda Springs Meadow. The station collects extensive weather data such as precipitation, temperature, snow depth, solar radiation, and wind speed. A close-up photo of the station shows some of the sensors needed to collect these data (Figure 1).

NPS / Jeff Balmat
Two interpretive signs were also installed to explain why the station was located in Soda Springs Meadow and why it is important to monitor weather and climate (Figure 2). This station is one of numerous stations that SIEN staff will use to monitor and report on trends in temperature, precipitation, and snowpack.
A report summarizing and evaluating current and historic weather data sources in and near DEPO is available (Balmat and Scott 2010). These local weather data will become increasingly valuable over time, enabling analyses of climatic trends to be done.
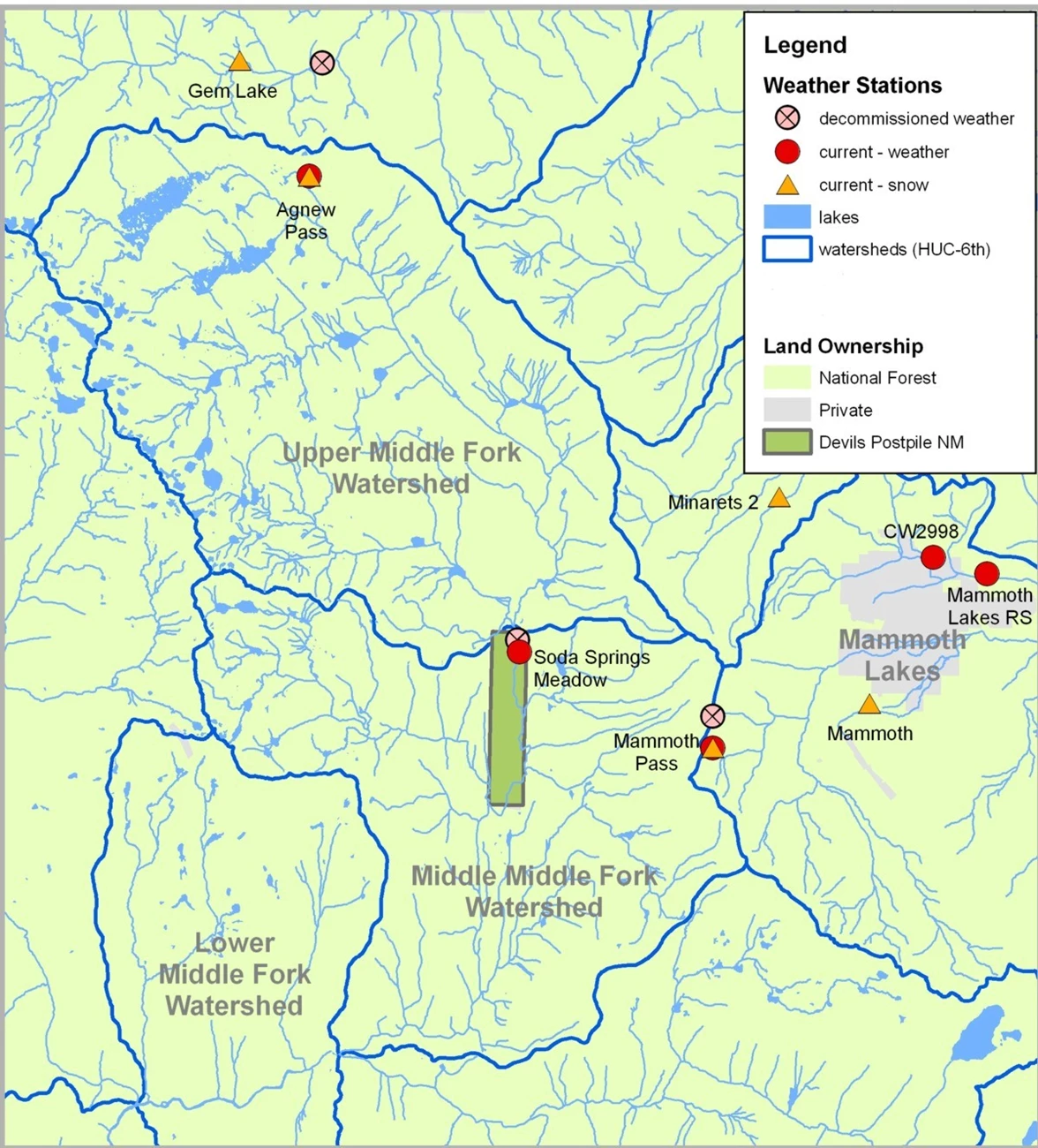
Longer term climate records of weather can be obtained from the stations located on U.S. Forest Service lands outside of the monument, such as Mammoth Pass, Agnew Pass, or Green Mountain (Figure 3). Data from weather stations operated by the Mammoth Mountain Ski Area can be accessed at: Mammoth Mountain Weather (westernweathergroup.com).

Discussion
Weather monitoring provides information about climate drivers that influence the critical surface water and groundwater resources at DEPO, and the biological communities that depend on them. The functioning and resilience of water-dependent features and communities at DEPO are closely tied to local and regional climate and water dynamics.
Weather and climate information can be used to help interpret changes in other resources and processes that are monitored at DEPO (such as stream and wetland water dynamics, wetlands vegetation and invertebrates, and bird populations). These data will contribute to the long-term understanding of climate in the Southern Sierra Nevada, allow fire managers to predict how a wildfire might spread over the landscape, provide information for California water managers to predict water availability for the local growing seasons, and contribute to the understanding of other ecosystem processes in the monument
and the surrounding US Forest Service lands.
The existence of a highly visible weather station and online realtime weather data present excellent opportunities for interpretation of weather, climate, climate change, snowpack, streamflow, and other related topics for the monument’s visitors and neighboring communities.
References
Balmat, J. and D.K. Scott. 2010. Weather data inventory, Devils Postpile National Monument. Natural Resource Report NPS/SIEN/NRDS—2010/113. National Park Service, Fort Collins, Colorado.
Additional Information
Western Regional Climate CenterCalifornia Data Exchange Center – DEPO weather data online
NPS Sierra Nevada Inventory & Monitoring Network
