Last updated: January 24, 2022
Article
2021 Weather In Review: Fort Necessity National Battlefield

NPS / Victoria Stauffenberg
This brief provides county-scale weather data from Fayette County, PA, including data from 1895–2021 (i.e. period of record). Data and analyses herein are courtesy of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) Climate at a Glance Program.
Weather vs. Climate
First of all, what is the difference between weather and climate? Weather consists of the short-term (minutes to months) changes in the atmosphere. Weather is what is happening outside at this very moment, be it rain, snow, or just a warm sunny day. Climate is what you expect to see based on long-term patterns of over 30 years or more. An easy way to remember the difference is that climate is what you might expect, like a hot summer, and weather is what you get, like a warm rainy day.
The following information includes a discussion of 2021 weather placed in the context of long-term climate (i.e. how did 2021 compare to a "normal" year?).
2021 Summary
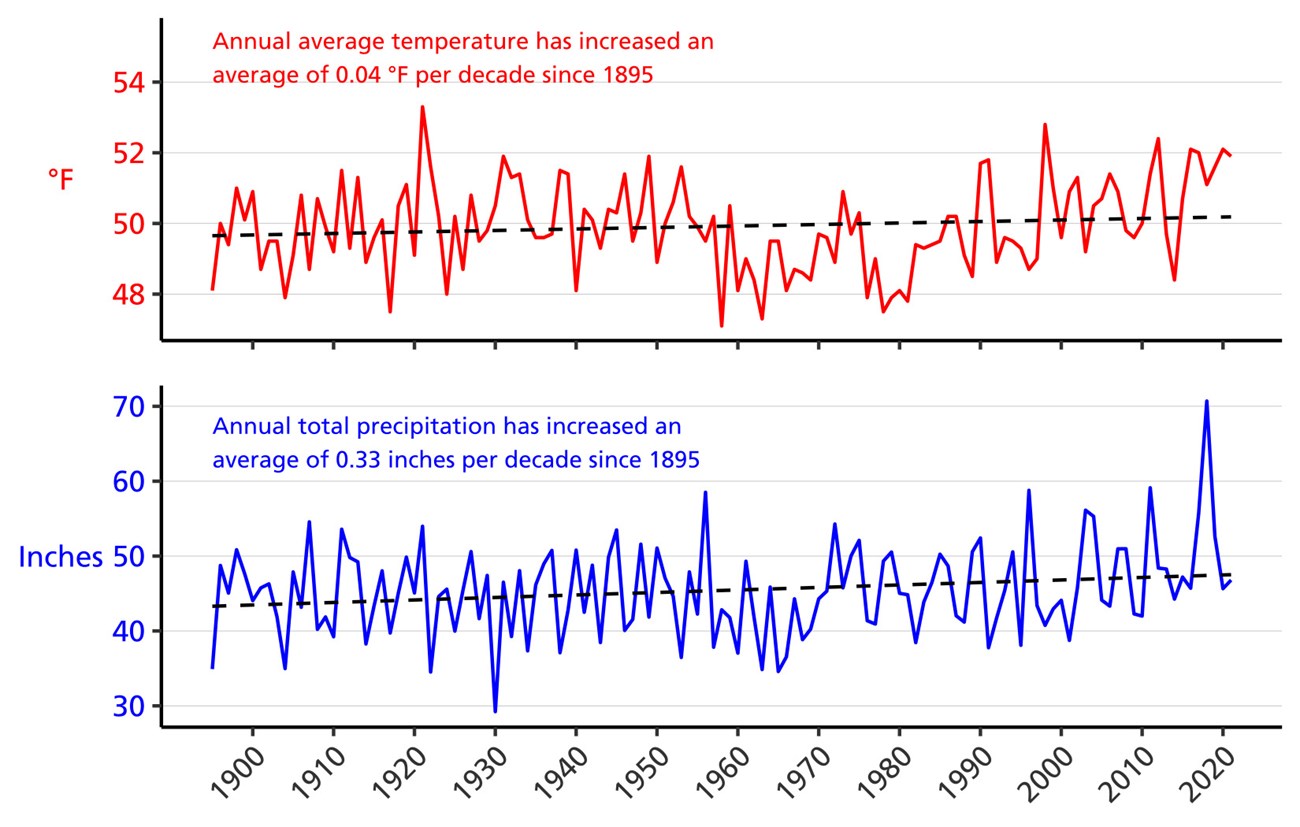
In all, 2021 was very warm but had near-normal total precipitation. The year ended as the 7th warmest and 49th wettest on record. Data indicate that over the long term, annual average temperature and annual total precipitation have both increased (+0.04 °F per decade and +0.33 inches per decade, respectively).Temperature
In total, 2021 was the 7th warmest year ever recorded at the park with three out of four seasons being warmer than normal (Figure 1). Nine months had higher than normal temperatures with March, October, and December all being more than 4.5 °F above long-term averages (Table 1).
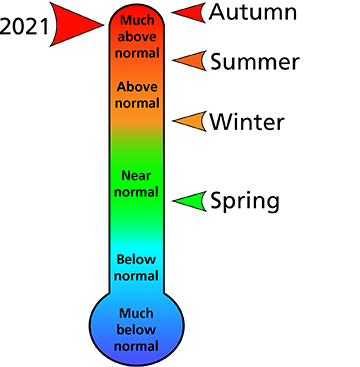
| Month/Year | Average temperature (°F) | Departure from long-term average (°F) |
|---|---|---|
| January | 29.9 | +2.1 |
| February | 28.1 | -1.3 |
| March | 43.0 | +4.6 |
| April | 50.3 | +1.2 |
| May | 57.0 | -2.1 |
| June | 67.9 | +0.8 |
| July | 71.1 | +0.2 |
| August | 72.3 | +2.9 |
| September | 64.6 | +1.2 |
| October | 57.9 | +5.7 |
| November | 39.6 | -1.3 |
| December | 40.5 | +9.2 |
| 2021 | 51.9 | +2.0 |
Precipitation
In total, it was a slightly wet year for precipitation, largely due to a very wet summer (Figure 2). The year ended as the 49th wettest on record. In all, 46.8 inches of precipitation fell, 1.4 inches more than the long-term average (Table 2).
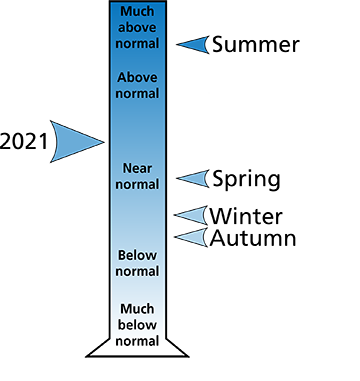
| Month/Year | Total precipitation (in.) | Departure from long-term average (in.) |
|---|---|---|
| January | 2.00 | -1.52 |
| February | 3.06 | +0.09 |
| March | 4.36 | +0.46 |
| April | 3.24 | -0.68 |
| May | 4.97 | +0.66 |
| June | 4.49 | -0.23 |
| July | 4.83 | +0.09 |
| August | 5.38 | +1.22 |
| September | 6.12 | +2.63 |
| October | 3.36 | +0.26 |
| November | 1.41 | -1.74 |
| December | 3.58 | +0.15 |
| 2021 | 46.80 | +1.40 |
Temperature and Precipitation Trends
(1895-2021)
Data for Fayette County, PA indicate that annual average temperature has increased approximately +0.04 °F per decade and annual total precipitation has increased approximately +0.33 inches per decade since 1895 (Figure 3).National Park Service scientists have forecast future changes in climate too. Models estimate that by 2100, annual average temperature at the park will increase by 3.1–9.2 °F (from a best-case to worst-case scenario, respectively). Annual total precipitation is expected to increase by 6–12% (see Gonzalez et al., 2018 for details).
Climate Change
Today's rapid climate change challenges national parks in ways we've never seen before. Wildlife migrations are altered, increasingly destructive storms threaten cultural resources and park facilities, habitat is disrupted—the list goes on. Go to the NPS Climate Change site to discover how climate change is affecting our nation's treasures, what the National Park Service is doing about it, and how you can help.For more information, contact Mid-Atlantic Network Biologist, Jeb Wofford or Eastern Rivers and Mountains Network Program Manager, Matt Marshall.
