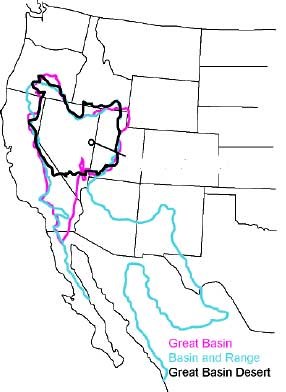
NPS Image What is the Great Basin?Defining the Great Basin begins with a choice: are you looking at the way the water flows (hydrographic), the way the landscape formed (geologic), or the resident plants and animals (biologic)? Each of these definitions will give you a slightly different geographic boundary of the Great Basin, but the hydrographic definition is the most commonly used. The Hydrographic Great Basin is a 200,000 square mile area that drains internally. All precipitation in the region evaporates, sinks underground or flows into lakes (mostly saline). Creeks, streams, or rivers find no outlet to either the Gulf of Mexico or the Pacific Ocean. The region is bounded by the Wasatch Mountains to the east, the Sierra Nevada to the west, and the Snake River Plain to the north. The south rim is less distinct. The Great Basin includes most of Nevada, half of Utah, and sections of Idaho, Wyoming, Oregon, and California. The term "Great Basin" is slightly misleading; the region is actually made up of many small basins. The Great Salt Lake, Pyramid Lake, and the Humboldt Sink are a few of the "drains" in the Great Basin. The Basin and Range region is the product of geological forces stretching the earth's crust, creating many north-south trending mountain ranges. These ranges are separated by flat valleys or basins. These hundreds of ranges make Nevada the most mountainous state in the country. The Great Basin Desert is defined by plant and animal communities. The climate is affected by the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada and Cascade Mountains. It is a temperate desert with hot, dry summers and snowy winters. The valleys are dominated by sagebrush and shadescale. The biologic communities on the mountain ranges differ with elevation, and the individual ranges act as islands isolated by seas of desert vegetation. Because the Great Basin exhibits such drastic elevation changes from its valleys to its peaks, the region supports an impressive diversity of species, from those adapted to the desert to those adapted to forest and alpine environments. Great Basin National Park preserves a small representative piece of this entire region. |
Last updated: April 22, 2021
