Part of a series of articles titled African American Households.
Article
The Nash Site
Historical Background
NPS
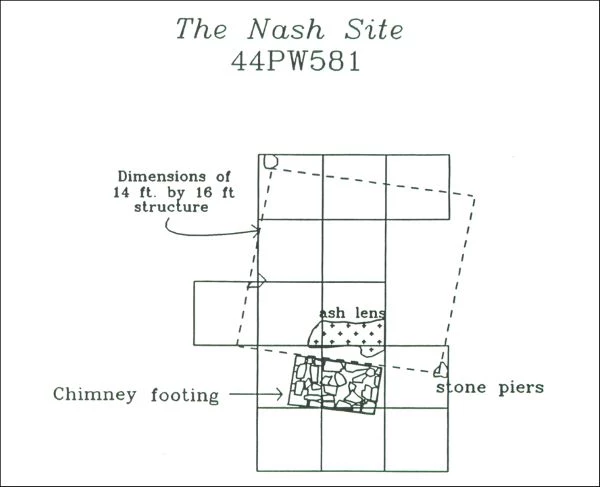
The Nash site was discovered during a 1990 archeological survey. Historical evidence indicates that the site was occupied by an African-American family, Philip Nash and his wife and children, for a relatively short time span from the 1870s to 1880s. Historically, the Nash site was located on a tract of land owned by the residents of the nearby Brownsville Plantation. Today, the remains of the dwelling consist of the stone chimney footing and stone piers to support a structure.

NPS
Archeological Excavations

NPS
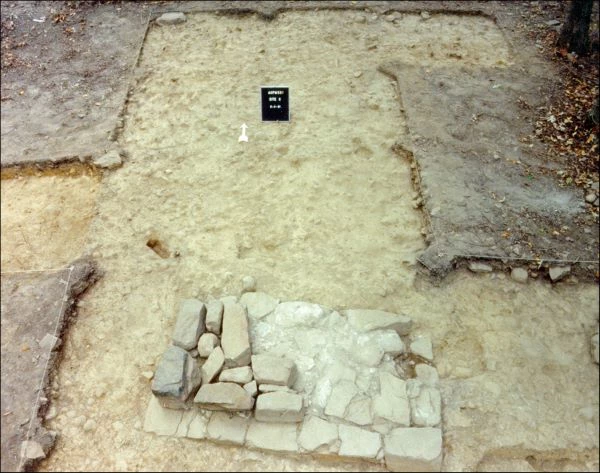
During the 1990 archeological survey, project archeologists discovered the remains of a chimney and a nearby depression related to the house. Archeological investigations at the Nash site occurred in 1991 and revealed the foundations of a 14-by-16 foot structure, most likely a one and one-half story frame building. Artifacts found during the excavations include ceramics, glass, architectural debris, buttons, a single blue bead, gaming pieces, and quartz crystals. The material culture indicates that the site was occupied during the 1870s to 1880s.

NPS
NPS
Last updated: April 20, 2020
